

- #Mac address assignment by manufacturer serial number#
- #Mac address assignment by manufacturer code#
- #Mac address assignment by manufacturer mac#
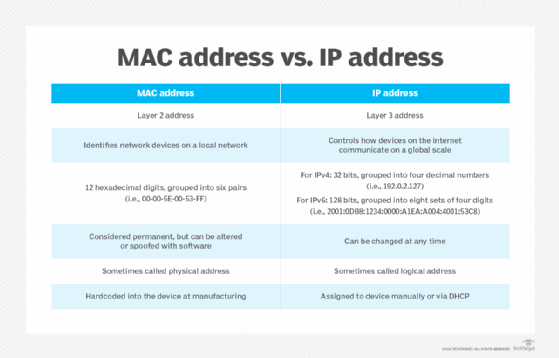
It is the combination of the OUI and the vendor-assigned number that ensures that no two network adapters have the same MAC address. The vendor-assigned portion of the MAC address is just that, the alphanumeric identifier assigned by the vendor. DHCP also usually relies on MAC addresses to manage the unique assignment of IP addresses to devices. The OUI is administered by the IEEE and identifies the vendor of the network adapter. indicates the manufacturer is Intel Corporation. The manufacturer then assigns a unique value for the last 3 bytes, which ensures that every MAC address is globaly unique. Manufacturers agree to give all NICs a MAC address that begins with the assigned OUI.
#Mac address assignment by manufacturer code#
The OUI is 00-08-a1, and the vendor-assigned number is 08-c8-13. Every network card manufacturer gets a universally unique 3-byte code called the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI). This MAC address is used for the Fast Ethernet adapter on the computer in question. The MAC address on a computer might look like this: 00-08-a1-08-c8-13. It is 48 bits (6 bytes) long and is made up of two parts: the organizational unique identifier (OUI) and the vendor-assigned address, as illustrated in Figure 5-1.
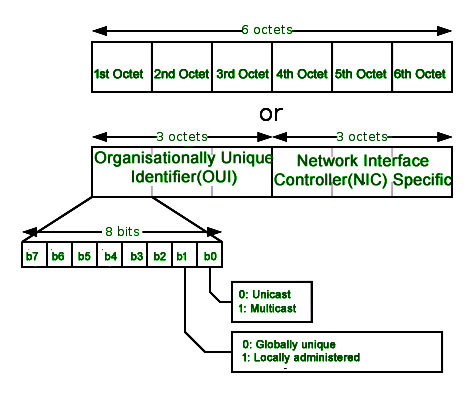
In IEEE 802 standard, Data Link Layer is divided into two sublayers. Each address can be stored in hardware, such as the card's read-only memory, or by a firmware mechanism. MAC Address is also known as Physical Address of a network device. MAC addresses are primarily assigned by device manufacturers, and are therefore often referred to as the burned-in address, or as an Ethernet hardware address, hardware address, or physical address. the physical address is used to identify a device in computer networks. Interface cards (nics) by the manufacturer of the hardware. It overrides the address assigned by device manufacturers. MAC Addresses are unique 48-bits hardware number of a computer, which is embedded into network card (known as Network Interface Card) during the time of manufacturing. Mac address is assigned by the ra ieee registries to the vendor, assign only the first three bytes of the allocation, the three bytes assigned their own. You may assign this address to a device used by network administrator. LAA is an address that changes the MAC address of the adapter. For this discussion of LAN environments, the physical address (also known as the Media Access Control address) is relevant.Ī MAC address is the physical address of the device. The remaining octets of the MAC address is assigned by manufacturer.
Two types of addresses are found in a network: the logical (OSI model Layer 3, network) and the physical (OSI model Layer 2, data link). To be a part of any network, you must have an address so that others can reach you.

#Mac address assignment by manufacturer serial number#
Info: Unable to generate a WWN, No more MAC address available to generate WWN.The MAC address is the unique serial number burned into each network adapter that differentiates the network card from all others, just as your house number is unique on your street and identifies your home from all others. Netapp-cluster1::> network interface create -vserver SAN_vserver1 -lif fcp1 -role data -data-protocol fcp -home-node node1 -home-port 0a Netapp-cluster1::> vserver fcp create -status-admin up -vserver SAN_vserver1Įrror: command failed: Unable to assign a unique WWNN for SAN_vserver1 At this time SAN LIFs will no longer be created normally.Įrror messages output is similar to the following: Storage controllers with MAC addresses from the new pool that are reverted to versions of ONTAP prior to those listed in the above section and joined to existing ONTAP clusters will continue to function normally until such time as the final storage controller from the old MAC address pool is removed. Storage controllers with MAC addresses from the new pool running versions of ONTAP prior to those listed in the above section will not be able to provision SAN LIFs. The assignment information is stored in the system's root volume. Data ONTAP uses the on-board port MACs to generate Fibre Channel World Wide Names (WWNs) for data LIFs when using the FCP or FC-NVMe protocol and has an integrity check to verify the on-board MAC is allocated from a known NetApp OUI. When the Fibre Channel service is initially licensed and enabled on your storage system, the FC target and initiator adapters are assigned WWPNs, which persist through head upgrades and replacements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
